Global Intangible Low-Taxed Income
Global Intangible Low-Taxed Income
Imposed by the Tax Cut and Jobs Act of 2017, code IRC 951A for Global Intangible Low-Taxed Income, GILTI, was introduced to assist in preventing tax evasion by controlled foreign corporations, CFCs, where a U.S. citizen is at least a 10% direct or indirect shareholder. GILTI is the income earned abroad by CFCs from their intangible assets such as the company’s copyrights, trademarks, and patents. The goal is to prevent companies from moving their intangible assets and profits to other countries with lower tax rates than what the United States enforces (21%). Foreign Taxation can get complex, and you need an experienced Tax professional like Kislay Shah CPA to guide you. Please reach out to Kislay via email at kislay@shahcpaus.com or by calling 646-328-1326.
How is GILTI Calculated?
Following the above equation, the tested income or the gross income/loss is deducted by 10% of the qualified bU.S.iness asset investment, QBAI, reduced by interest expense. Each number U.S.ed in the equation above is carefully configured by their own calculations.
Situational Applications
1. A C Corporation registered in DE state owns 100% shares of a foreign entity in India. The foreign entity in India is a Private Limited Company.
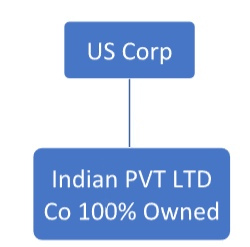
Be advised that there are additional disclosure requirements that apply.
- Is GILTI tax going to apply since the foreign entity is a CFC?
Yes, the GILTI tax will apply and is reportable on Form 8992. The U.S. entity can claim GILTI exemption if the foreign entity has losses or if the tax rate for the foreign entity (High Tax Exemption) is greater than 18.9% (90% or 21%). File an election for claiming GILTI exemption if applicable.
Corp’s can take 50% deduction resulting in effective rate of 10.5%. There is no 50% reduction in GILTI rate for individuals.
U.S. Corp can claim foreign tax credit (FTC) by filing form 1118 with 1120. The FTC is limited to 80% of tax paid by the foreign entity.
- What forms are required to be filed with 1120 tax return in addition to 5471,5472, and FBAR?
Annual 5471 is required to be filed with category 4 or 5. Also mark category 2 and 3 in the year of formation. No 5472 required since no foreign shareholder. FBAR and 8938 reporting for indirect foreign accounts holdings.
- The profits of the Indian entity are taxed in India. Are these profits subject to tax in the U.S. or only the dividend distribution by an Indian entity to the U.S. parent subject to tax in the U.S.?
Dividend distribution is not subject to taxes U/S 245A of the IRC at the U.S. Corp owner level as it will be taxed when dividend distribution to the owners.
- How do we report the dividend distribution?
It will reduce the retained earnings of the foreign entity.
- Also, file Form 926 – Report cash transfers of capital and transfers for payment of invoices by U.S. Corp to Indian Corp.
2. A C-Corporation registered in DE state is 100% owned by a foreign entity in India.
The foreign entity in India is a Private Limited Company.
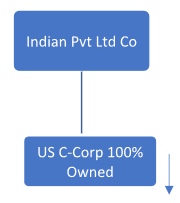
Be informed that there are additional disclosure requirements required.
- What forms are required to be filed with 1120 tax return in addition to Forms 5471, 5472 and FBAR?
No need to file 5471 since it’s not a CFC.
File Form 5472 – Required to report foreign 25% ownership/shareholders for each of the shareholders with 25% or greater ownership.
File FBAR and 8938 if required.
- The profits of the Indian entity are taxed in India. Are the profits of only the U.S. subsidiary subject to tax in the U.S.?
Yes.
- How should the dividend distribution by the U.S. subsidiary to the Indian parent Company br reported in the U.S.?
Dividend distribution by the U.S. Corp to Indian Corp is subject to tax withholding at a lower rate of 15% instead of 30% based on the U.S./India tax treaty.
- Under the Corporate Transparency Act, starting 2024 the downward attribution rules will apply if the Indian parent company has other subsidiaries in other countries besides U.S. File 5471 for the other foreign subsidiary. If more than one shareholder only one shareholder is required to report and the other can report.
3. An Indian Private Limited Company is owned by two U.S. individual shareholders
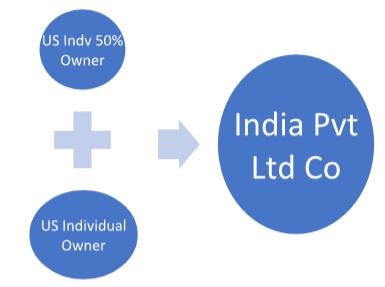
Note that there are supplementary disclosure requirements.
- What forms are required to be filed with 1040 tax return in addition to 5471, 5472 and FBAR?
No need to file 5472.
Report on Form 5471 with category 5. Also mark category 4 if the individual is greater than 50% shareholder or for related shareholders if the combined shareholding results in greater than 50% shareholding. Only one shareholder with greater than 50% shareholding is required to file 5471.
File FBAR to report disclosure of foreign bank accounts and 8938 if required.
- Is GILTI tax going to apply since the foreign entity is a CFC?
Yes, the GILTI tax will apply and is reportable on Form 8992.
The U.S. individuals can claim GILTI exemption if the foreign entity has losses or if the tax rate for foreign entity (High tax exemption) is greater than 18.9% (90% of 21%).
File an election for claiming GILTI exemption if applicable.
There is no 50% reduction in GILTI rate for individuals.
File Form 926 for all capital contributions.
4. A U.S. single member LLC (U.S. disregarded entity) is owned 100% by a foreign Individual.
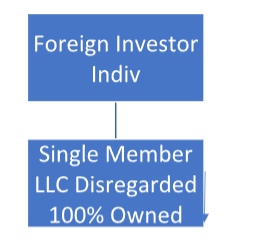
Be advised that there are additional disclosure requirements.
- What tax forms are required to be filed?
File Form 5472 to report to foreign owner of U.S. entity. Also prepare 1120 Proforma and mail 1120 Proforma and 5472 to the applicable 5472 mailing address.
Foreign Individual owner required to file 1040NR to report U.S. sourced income. Permanent establishment will result in U.S. sourced income. The income is not subject to tax in U.S. if the services are performed outside U.S..
Capital Gains on assets other than real estate are not subject to taxes to NR alien.
- Subpart F Income involves CFCs (Controlled Foreign Corporations) that accumulate certain specific types of income (primarily passive income). When a CFC has Subpart F income under IRC Section 952, that means the U.S. shareholders may have to pay tax on
the earnings.
